Back in May 2020, Google announced a set of user-focused metrics called Core Web Vitals (CWV). Joining hundreds of other ranking signals that Google uses in its algorithm, this new ranking signal rolled out in June 2021 and focuses specifically on-page user experience.
What is Core Web Vitals?
Backlinko summarised it very succinctly: “Core Web Vitals are a subset of factors that will be part of Google’s “page experience” score (basically, Google’s way of sizing up your page’s overall UX.”
CWVs measure a site's health in terms of user experience by using three main metrics, visual loading, interactivity and visual stability. These metrics are then ranked into three scores - Poor, Need improvement and Good and are separated by device type (mobile and desktop).
The data for CWV measurements come from the Chrome User Experience Report (CrUX) and are assessed for each page individually. However, Google’s John Mueller says that signals from sections of a site, or the overall site may sometimes be used.
Why Are Core Web Vitals Important?
Core Web Vitals will make up a huge part of your page experience score and are officially used as one of over 200 ranking factors.
It’s therefore important you have a grasp on these metrics and how you can ensure your site is user-friendly.
The core web vitals are split into three main metrics measuring page loading, interactivity and visual stability. These metrics are as follows.
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
The largest contentful paint (LCP) is used to measure the time between a user landing on a page and then the largest content element being loaded in. Basically, how long a page takes to load the majority of the content on-screen.
Usually, the largest element will probably be the featured image. However it could also be a <h1>, <img>, <image> inside an <svg> or even a block of text.

Ideally, a score of less than 2.5 seconds will register a good score, whereas anything over 4 seconds will be ranked as poor.
Reductions in LCP can have a real impact on many factors. In a study by Google, with each 100ms reduction in LCP, the web conversion rate increased by 1.3%!
First Input Delay (FID)
First Input Delay (FID) is the time between the first input event. Put simply, it’s the time it takes for a user to be able actually to interact with the page. Technically, it’s a page speed measurement, however, it goes a little deeper than that, measuring the time it takes for visitors actually to perform an action.
Interactions here can include clicking on a link, entering information into a field, interacting with the navigation or menu and other similar interactions.
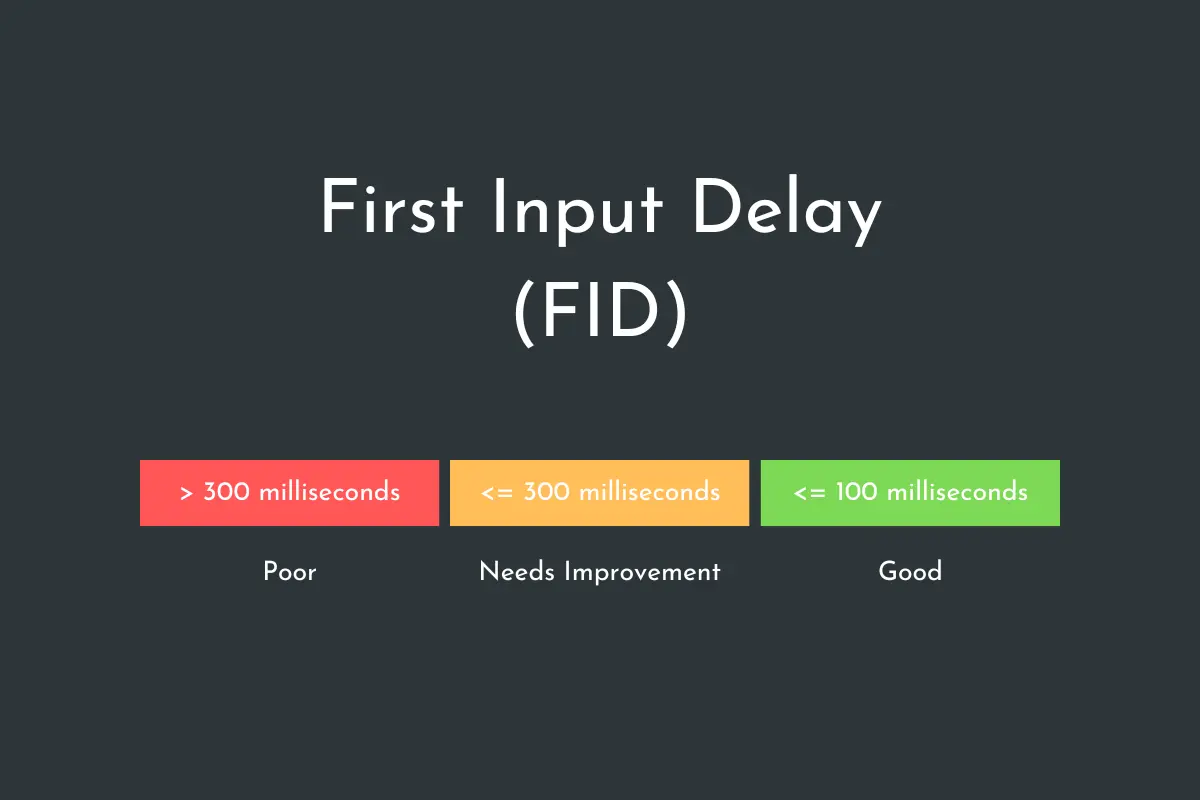
To achieve a score of good here, the time between the input event and the reaction should be less than 100 milliseconds. Anything over 300 milliseconds will be ranked as poor.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) measures the visual stability of a page and the amount that a page layout changes upon a user landing on a page. Put simply, CLS focuses on how much your page moves around when loading. There’s nothing worse than attempting to click on something and clicking on something else because of a layout shift during page load.

Common causes of cumulative layout shift can include images that have no set dimensions, embeds, iframes without dimensions and ads. To achieve a score of good, CLS needs to be equal to or less than 0.1 and anything over 0.25 will be classed as poor.
Google has stated that Yahoo! JAPAN reduced their CLS by 0.2 which resulted in a 15% increase in page views per session, longer session durations and a decrease in bounce rate. It has also been noted that reducing CLA significantly uplifted domain rankings.
Google Core Web Vitals Test
You can check your CWV score using Google’s Page Speed Insights. You can also see them reported within the ‘experience’ section of your Google Search Console account.
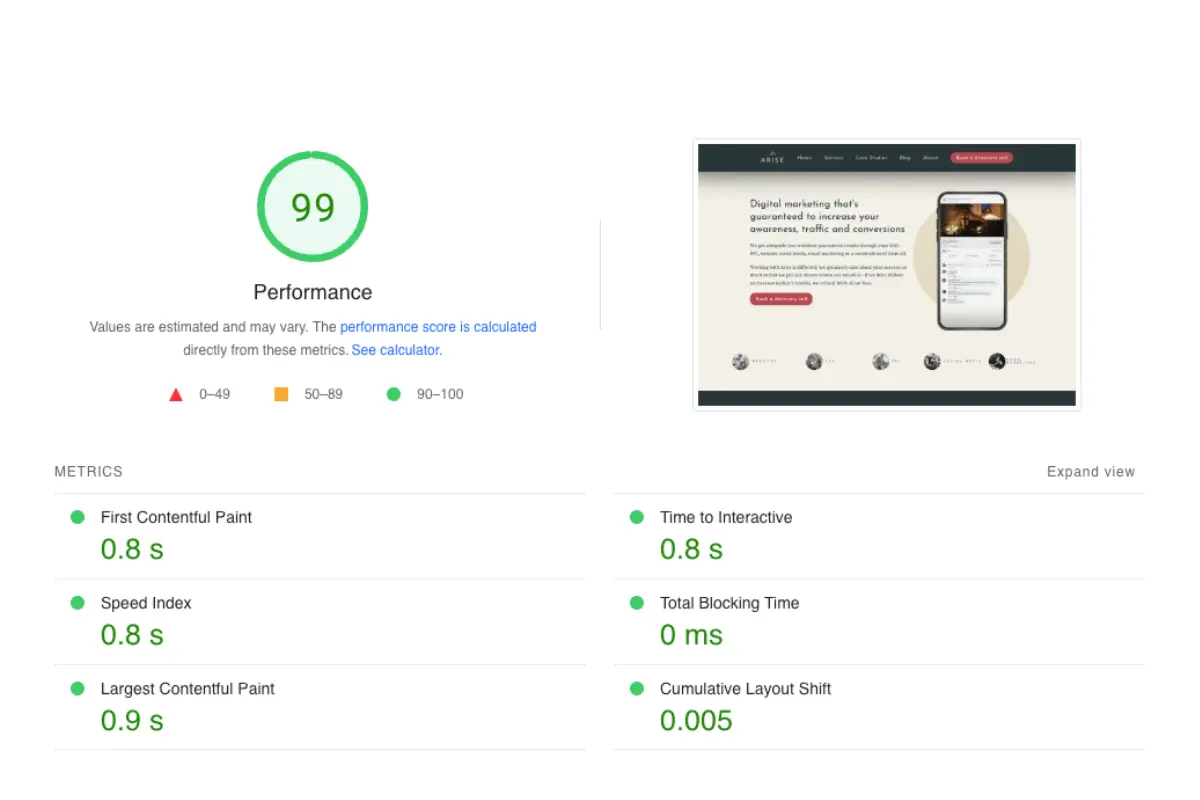
It’s important to note that only indexed URLs will appear in this report and that data is assigned to the actuarial URL, not the canonical URL.
Conclusion
The user experience should already be a primary focus of any website design, however, it’s now even more important from an SEO perspective.
Although noted to be small, these metrics are used as one of Google’s ranking factors and it’s, therefore, crucial your website is optimised for CWV.
It’s also, however, important to remember that these metrics may change over time.